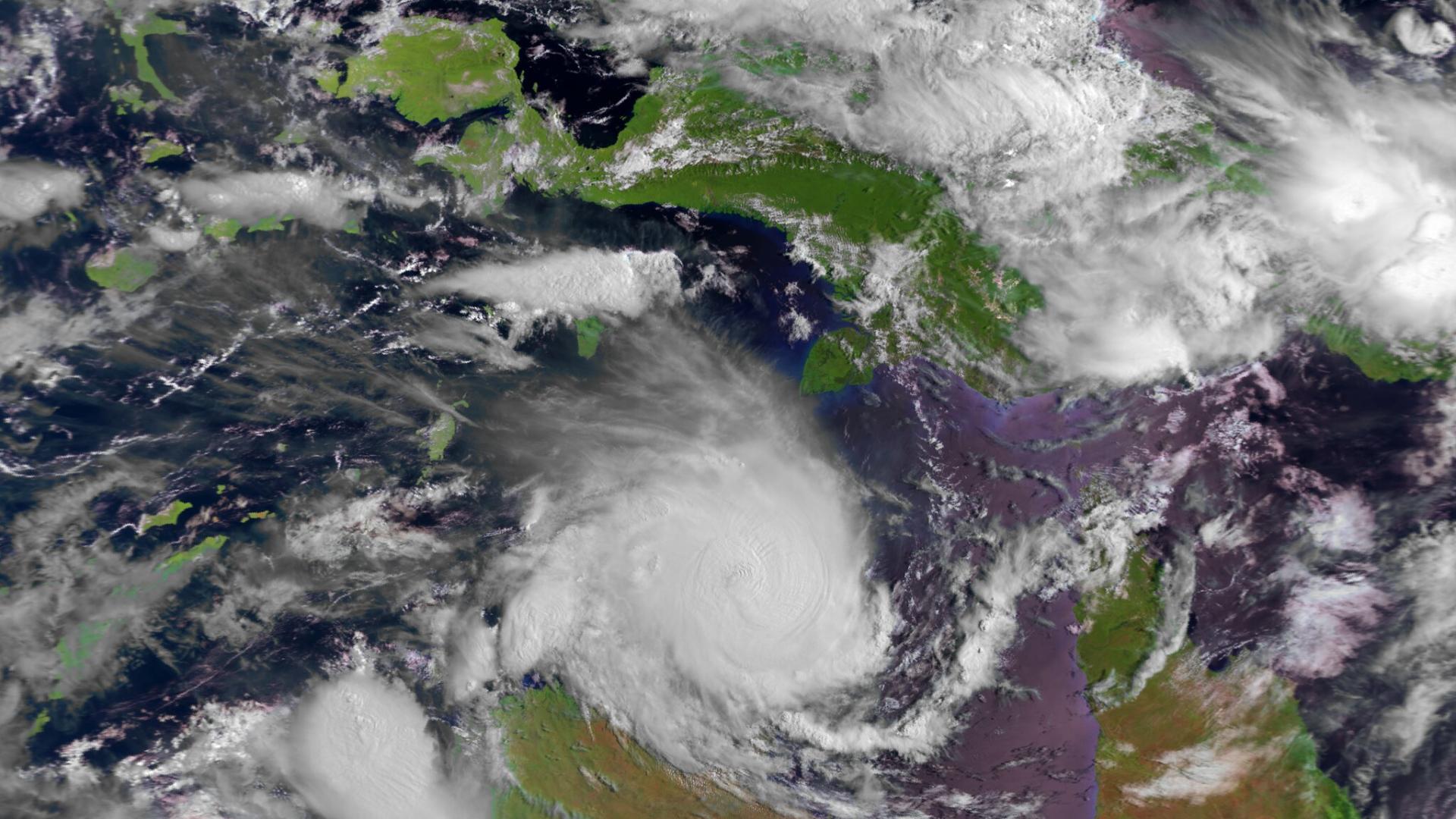
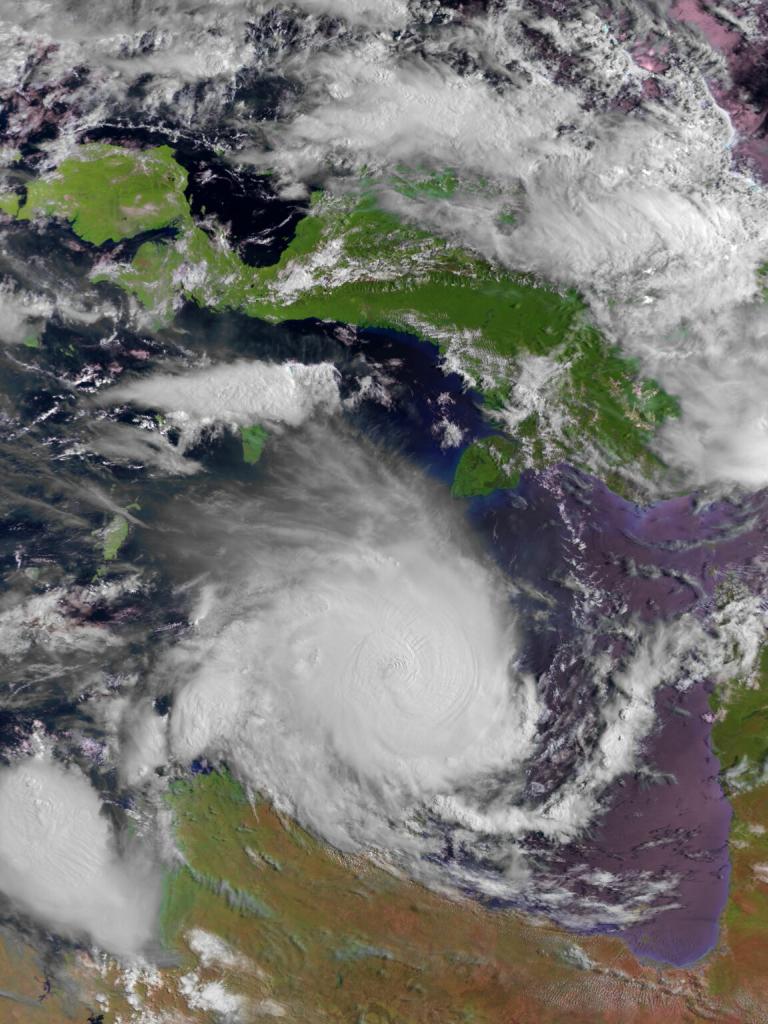
13 February 2025
24 April 2023
The Committee on Earth Observation Satellites (CEOS) was established in September 1984 in recognition of the multidisciplinary nature of space-based Earth observations and the value of coordinating international efforts. CEOS agencies communicate, collaborate, and exchange information on Earth observation activities, spurring useful partnerships.
The Global Climate Observing System (GCOS) was established in 1992 to ensure that the observations and information required to address climate-related issues were obtained and made available to all potential users.
The intergovernmental Group on Earth Observations (GEO) is leading a worldwide effort to build a Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS).