17 May 2022
02 April 2020
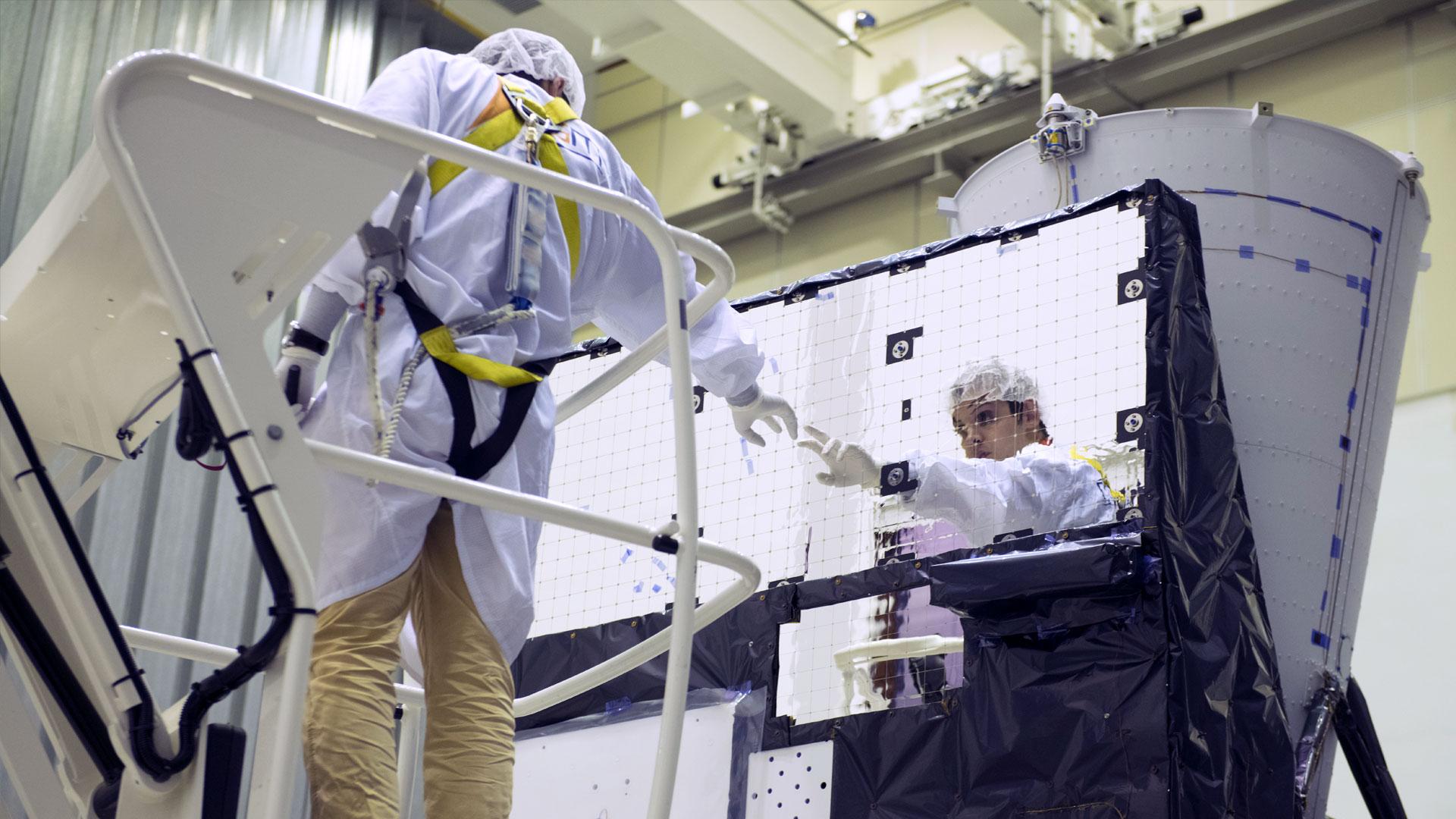
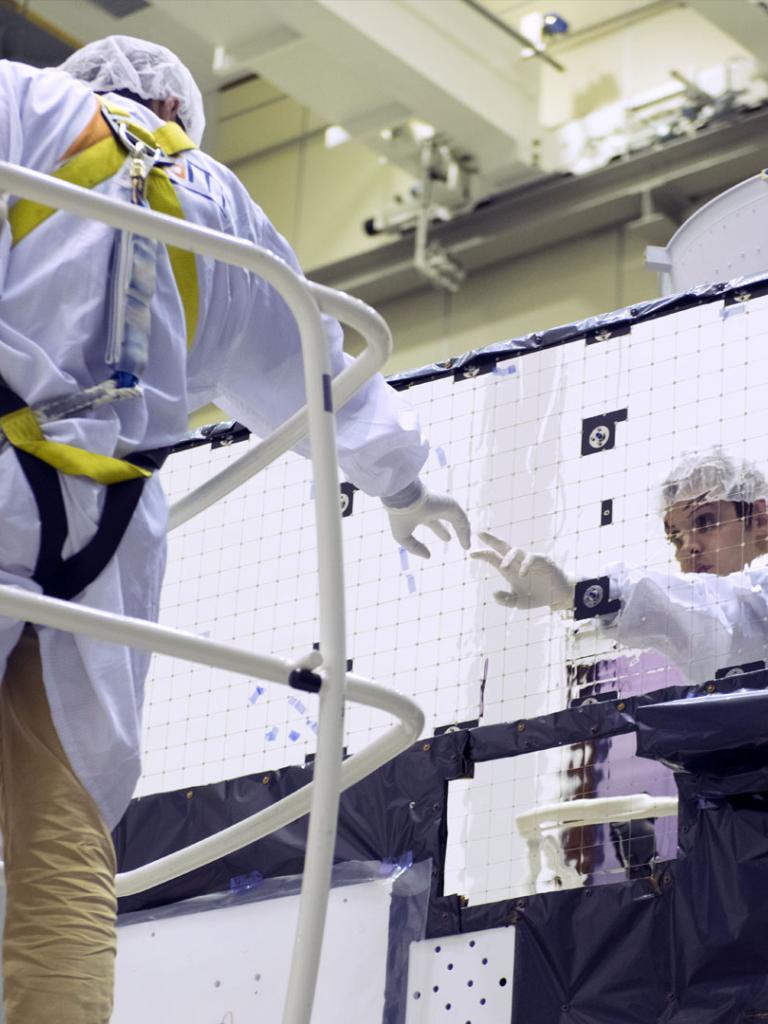
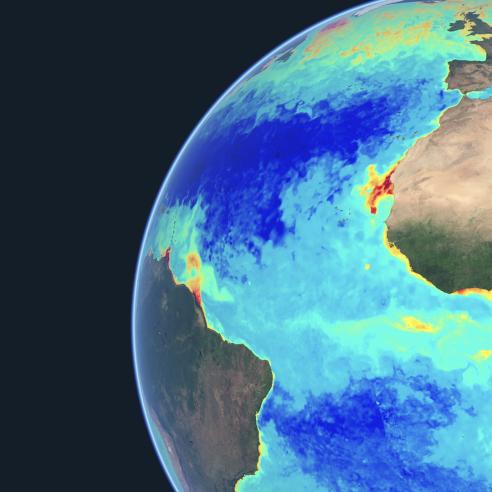
The Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) programme was fully approved by EUMETSAT Member States in February 2011, thereby establishing the first pillar of EUMETSAT's future in the 2020-2040 timeframe. This is a promise for the future of operational meteorology in Europe and Africa, in particular with regard to nowcasting and very short range forecasting of high-impact weather.
The EUMETSAT Polar System Second Generation (EPS-SG) is the second pillar of EUMETSAT's future, expected to continue the global observations of EPS in the 2020-2040 timeframe, and to enhance the critical inputs delivered to Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models. The main priorities of the programme will be to support operational weather forecasting and to provide operational services in support of climate monitoring and new environmental services.
The cooperation model with ESA
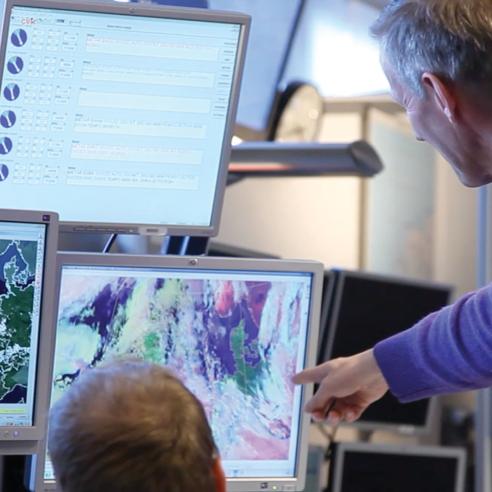
For all of our mandatory programmes, EUMETSAT develops new satellite systems in cooperation with ESA, in a model which makes best use of the respective competencies of both organisations. This model, together with a highly competitive European space industry, has made Europe the world leader in satellite meteorology.
ESA is responsible for the development of satellites which fulfil the user and system requirements defined by EUMETSAT, and for the procurement of recurrent satellites on its behalf. EUMETSAT develops all ground systems required to deliver products and services to users and to respond to their evolving needs, procures launch services, and operates the full system for the benefit of users.
This process also involves European industry through contracts with ESA and EUMETSAT, capitalising on upstream European research and development, and stimulates the competiveness and growth of European industry.